
If we were to scan this local area network with nmap, we would want to scope out all the addresses in the network's range, which means 192.168.4.1, 192.168.4.2, 192.168.4.3, 192.168.4.4, and so on, all the way to 192.168.4.255. That means 192.168.4.5 is the ip address of that specific machine, while the /24 at the end indicates the address space for the LAN's subnet, which in this case are all the addresses from 192.168.4.1 to 192.168.4.255. Notice in the ip addr output above, the ip address is: 192.168.4.5/24. Yours is likely something similar to this: for example, 192.168.1.123 or 10.0.0.56 etc. Here are a couple ifconfig and ip addr outputs posted by the Ubuntu Journeyman:Īs you can see here, the ip address for this machine is 192.168.1.4.5.
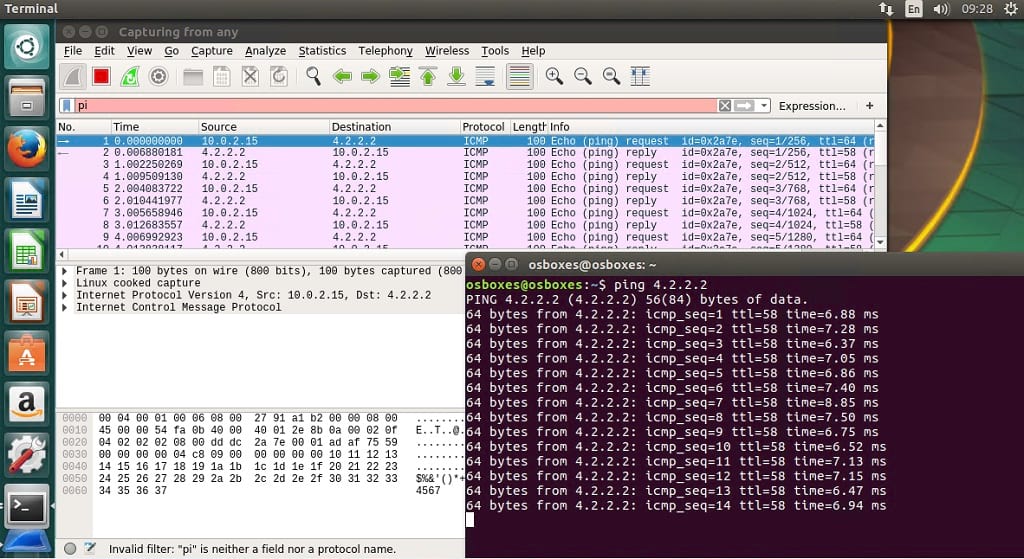
That is your ip address on your local area network. Identify the interface that is connected to the LAN (likely eth0), and make a note of the ip address indicated after "inet" for the ip addr command, or after "int addr:" for the ifconfig command. These commands will provide you will a wealth of information about your network interfaces. To access it from your administrator account, all you need to do is add "sudo" to the front of the command: sudo ifconfig.) In Kali, sensitive system commands like ifconfig have to be run as root. (Note that if you are using an administrator account inside Kali, which is considered a best practice, when a non-root user enters a command such as ifconfig into a terminal, the shell will likely respond by complaining "command not found". You could use, for example, the ip or ifconfig commands in a terminal: ip addr, or sudo ifconfig. There are a number of different ways to determine your ip address on a Linux distribution such as Kali. We'll then configure Wireshark and run a packet captures to get a sense for the normal traffic on the network, and then run another capture to analyze just how an nmap network scan works.īefore we can scan the network with nmap, we need to identify the ip address range we would like to examine. We are first going to use nmap to see if we can identify any such devices on the network, and perhaps detect one or two that we did not think or know were connected to it. There may also be more computers or cell phones connected to it, and maybe even your television, refrigerator or coffee maker! At the very least, we know there will be at least three: the Kali guest, the host machine you are running Kali on, and your router. Do you happen to know how many devices are currently connected to your home network? Can you identify all of them off the top of your head? Try to do so, and make a list of them. Dumpcap is a command line network traffic monitor, and Wireshark provides a powerful and versatile graphical interface to monitor network traffic and analyze network packet capture files. Nmap is a command line network scanner, and Zenmap is a graphical interface to nmap. These will come in handy in our eventual testing lab, but they can obviously also be used to explore your home local area network as well. In particular, we'll take a look at a set of tools that come bundled in Kali that can be used for network analysis: nmap/Zenmap and dumpcap/Wireshark. This article will show how some of the tools that come bundled in Kali can be used to explore your existing home computer network, and test whether you can successfully identify all the devices that are connected to it. But if you're like me, you're probably already itching to start playing with all the toys Kali has to offer, if you haven't already!
WIRESHARK MONITOR MODE VIRTUALBOX INSTALL
Finally, your Kali VM has a single network adapter running in bridged mode and you have set up an administrator account on the Kali instance.Ĭreating and configuring the virtual network setup outlined in the introduction, which we will do in part three of this series, requires a few more steps: we still have to download and install Metasploitable, set up the virtual network, etc. The Kali system has been fully updated and VirtualBox Guest Additions have been installed on it. If you followed along in part one, installing a Kali Linux virtual machine in VirtualBox, you have installed VirtualBox on the primary computer for your home lab and created a Kali Linux virtual guest on this host machine.
WIRESHARK MONITOR MODE VIRTUALBOX HOW TO
This article is part two in our tutorial series on how to set up a home hacking and security testing lab.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
